本文在前文 Spring Security 入门(三):Remember-Me 和注销登录 一文的代码基础上介绍Spring Security的 Session 会话管理。
Session 会话管理的配置方法
Session 会话管理需要在configure(HttpSecurity http)方法中通过http.sessionManagement()开启配置。此处对http.sessionManagement()返回值的主要方法进行说明,这些方法涉及 Session 会话管理的配置,具体如下:
invalidSessionUrl(String invalidSessionUrl):指定会话失效时(请求携带无效的 JSESSIONID 访问系统)重定向的 URL,默认重定向到登录页面。invalidSessionStrategy(InvalidSessionStrategy invalidSessionStrategy):指定会话失效时(请求携带无效的 JSESSIONID 访问系统)的处理策略。maximumSessions(int maximumSessions):指定每个用户的最大并发会话数量,-1 表示不限数量。maxSessionsPreventsLogin(boolean maxSessionsPreventsLogin):如果设置为 true,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求会被拒绝登录;如果设置为 false,表示某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求时失效并根据 expiredUrl() 或者 expiredSessionStrategy() 方法配置的会话失效策略进行处理,默认值为 false。expiredUrl(String expiredUrl):如果某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求时失效并重定向到 expiredUrl。expiredSessionStrategy(SessionInformationExpiredStrategy expiredSessionStrategy):如果某用户达到最大会话并发数后,新会话请求访问时,其最老会话会在下一次请求中失效并按照该策略处理请求。注意如果本方法与 expiredUrl() 同时使用,优先使用 expiredUrl() 的配置。sessionRegistry(SessionRegistry sessionRegistry):设置所要使用的 sessionRegistry,默认配置的是 SessionRegistryImpl 实现类。
Session 会话失效处理
当用户的 Session 会话失效(请求携带着无效的 JSESSIONID 访问系统)时,可以制定相关策略对会话失效的请求进行处理。
invalidSessionUrl 方法
☕️ 修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,配置 Session 会话失效时重定向到/login/page
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @EnableWebSecurity public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http.sessionManagement() .invalidSessionUrl("/login/page" ); } }
☕️ 设置 Session 的失效时间
Session 的失效时间配置是 SpringBoot 原生支持的,可以在 application.properties 配置文件中直接配置:
1 2 3 4 5 server.servlet.session.timeout =30m server.servlet.session.cookie.max-age =-1
注意: Session 的失效时间至少要 1 分钟,少于 1 分钟按照 1 分钟配置,查看源码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 public class TomcatServletWebServerFactory extends AbstractServletWebServerFactory implements ConfigurableTomcatWebServerFactory , ResourceLoaderAware private long getSessionTimeoutInMinutes () Duration sessionTimeout = this .getSession().getTimeout(); return this .isZeroOrLess(sessionTimeout) ? 0L : Math.max(sessionTimeout.toMinutes(), 1L ); } }
为了方便检验,在 application.properties 中配置 Session 的失效时间为 1 分钟:
1 2 server.servlet.session.timeout =60
☕️ 测试
浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入正确的用户名、密码(不选择“记住我”功能)成功登录后,重定向到首页面:
之后,等待 1 分钟,刷新页面,浏览器重定向到/login/page:
invalidSessionStrategy 方法
如果想要自定义 Session 会话失效处理策略,使用该方法传入自定义策略。
⭐️ 自定义 Session 会话失效处理策略 CustomInvalidSessionStrategy
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 package com.example.config.security.session;import com.example.entity.ResultData;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.security.web.DefaultRedirectStrategy;import org.springframework.security.web.RedirectStrategy;import org.springframework.security.web.session.InvalidSessionStrategy;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.servlet.http.Cookie;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;@Component public class CustomInvalidSessionStrategy implements InvalidSessionStrategy @Autowired private ObjectMapper objectMapper; private final RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy(); @Override public void onInvalidSessionDetected (HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException Cookie cookie = new Cookie("JSESSIONID" , null ); cookie.setPath(getCookiePath(request)); cookie.setMaxAge(0 ); response.addCookie(cookie); String xRequestedWith = request.getHeader("x-requested-with" ); if ("XMLHttpRequest" .equals(xRequestedWith)) { response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8" ); response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new ResultData<>(1 , "SESSION 失效,请重新登录!" ))); }else { redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/login/page" ); } } private String getCookiePath (HttpServletRequest request) String contextPath = request.getContextPath(); return contextPath.length() > 0 ? contextPath : "/" ; } }
⭐️ 修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,配置使用自定义的 Session 会话失效处理策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 @EnableWebSecurity public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter @Autowired private CustomInvalidSessionStrategy invalidSessionStrategy; @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http.sessionManagement() .invalidSessionStrategy(invalidSessionStrategy); } }
⭐️ 测试
浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入正确的用户名、密码(不选择“记住我”功能)成功登录后,重定向到首页面:
之后,等待 1 分钟,刷新页面,查看响应头:
同时,浏览器重定向到/login/page:
Session 会话并发控制
Session 会话并发控制可以限制用户的最大并发会话数量,例如:只允许一个用户在一个地方登陆,也就是说每个用户在系统中只能有一个 Session 会话。为了方便检验,在 application.properties 中将 Session 的过期时间改回 30 分钟:
1 2 server.servlet.session.timeout =30m
在使用 Session 会话并发控制时,最好保证自定义的 UserDetails 实现类重写了 equals() 和 hashCode() 方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Data public class User implements UserDetails private String username; @Override public boolean equals (Object obj) return obj instanceof User && this .username.equals(((User) obj).username); } @Override public int hashCode () return this .username.hashCode(); } }
我们前面实现了两种登录方式:用户名、密码登录和手机短信验证码登录,需要保证两种登录方式使用的是同一个 SessionAuthenticationStrategy 实例,也就是 MobileAuthenticationConfig 配置类中要有(1.4)的配置:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Component public class MobileAuthenticationConfig extends SecurityConfigurerAdapter < @Override public void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception MobileAuthenticationFilter filter = new MobileAuthenticationFilter(); SessionAuthenticationStrategy sessionAuthenticationStrategy = http.getSharedObject(SessionAuthenticationStrategy.class); filter.setSessionAuthenticationStrategy(sessionAuthenticationStrategy); } }
如果没有(1.4)的配置,MobileAuthenticationFilter 默认使用的是 NullAuthenticatedSessionStrategy 实例管理 Session,而 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter 使用的是 CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy 实例管理 Session,也就是说两种登录方式的 Session 管理是相互独立的,这是不应该出现的情况。
基本使用
场景一:如果同一个用户在第二个地方登录,则不允许他二次登录
✏️ 修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,配置用户最大并发 Session 会话数量和限制用户二次登录
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 @EnableWebSecurity public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http.sessionManagement() .invalidSessionStrategy(invalidSessionStrategy) .maximumSessions(1 ) .maxSessionsPreventsLogin(true ); .sessionRegistry(sessionRegistry()); } @Bean public SessionRegistry sessionRegistry () return new SessionRegistryImpl(); } @Bean public HttpSessionEventPublisher httpSessionEventPublisher () return new HttpSessionEventPublisher(); } }
✏️ 测试
第一个浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入正确的用户名、密码成功登录后,会重定向到/index:
第二个浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入相同的用户名、密码访问,重定向/login/page?error:
上述配置限制了同一个用户的二次登陆,但是不建议使用该配置。因为用户一旦被盗号,那真正的用户后续就无法登录,只能通过联系管理员解决,所以如果只能一个用户 Session 登录,一般是新会话登录并将老会话踢下线。
场景二:如果同一个用户在第二个地方登录,则将第一个踢下线
☕ 自定义最老会话被踢时的处理策略 CustomSessionInformationExpiredStrategy:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 package com.example.config.security.session;import com.example.entity.ResultData;import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.security.authentication.AuthenticationServiceException;import org.springframework.security.core.AuthenticationException;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.UserDetails;import org.springframework.security.web.DefaultRedirectStrategy;import org.springframework.security.web.RedirectStrategy;import org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionInformationExpiredEvent;import org.springframework.security.web.session.SessionInformationExpiredStrategy;import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;import java.io.IOException;@Component public class CustomSessionInformationExpiredStrategy implements SessionInformationExpiredStrategy @Autowired private ObjectMapper objectMapper; private final RedirectStrategy redirectStrategy = new DefaultRedirectStrategy(); @Override public void onExpiredSessionDetected (SessionInformationExpiredEvent event) throws IOException HttpServletRequest request = event.getRequest(); HttpServletResponse response = event.getResponse(); UserDetails userDetails = (UserDetails) event.getSessionInformation().getPrincipal(); String msg = String.format("用户[%s]在另外一台机器登录,您已下线!" , userDetails.getUsername()); String xRequestedWith = event.getRequest().getHeader("x-requested-with" ); if ("XMLHttpRequest" .equals(xRequestedWith)) { response.setContentType("application/json;charset=utf-8" ); response.getWriter().write(objectMapper.writeValueAsString(new ResultData<>(1 , msg))); }else { AuthenticationException e = new AuthenticationServiceException(msg); request.getSession().setAttribute("SPRING_SECURITY_LAST_EXCEPTION" , e); redirectStrategy.sendRedirect(request, response, "/login/page?error" ); } } }
☕ 修改安全配置类 SpringSecurityConfig,配置最老会话被踢时的处理策略
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 @EnableWebSecurity public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter @Autowired private CustomSessionInformationExpiredStrategy sessionInformationExpiredStrategy; @Override protected void configure (HttpSecurity http) throws Exception http.sessionManagement() .invalidSessionStrategy(invalidSessionStrategy) .maximumSessions(1 ) .maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false ) .sessionRegistry(sessionRegistry()) .expiredSessionStrategy(sessionInformationExpiredStrategy); } @Bean public SessionRegistry sessionRegistry () return new SessionRegistryImpl(); } @Bean public HttpSessionEventPublisher httpSessionEventPublisher () return new HttpSessionEventPublisher(); } }
☕ 测试
第一个浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入正确的用户名、密码成功登录后,重定向到/index:
第二个浏览器访问localhost:8080/login/page,输入相同的用户名、密码成功登录后,重定向到/index:
刷新第一个浏览器页面,重定向到/login/page?error:
原理分析
✌ AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter#doFilter
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 public abstract class AbstractAuthenticationProcessingFilter extends GenericFilterBean implements ApplicationEventPublisherAware , MessageSourceAware private SessionAuthenticationStrategy sessionStrategy = new NullAuthenticatedSessionStrategy(); public void doFilter (ServletRequest req, ServletResponse res, FilterChain chain) throws IOException, ServletException HttpServletRequest request = (HttpServletRequest)req; HttpServletResponse response = (HttpServletResponse)res; if (!this .requiresAuthentication(request, response)) { chain.doFilter(request, response); } else { if (this .logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this .logger.debug("Request is to process authentication" ); } Authentication authResult; try { authResult = this .attemptAuthentication(request, response); if (authResult == null ) { return ; } this .sessionStrategy.onAuthentication(authResult, request, response); } catch (InternalAuthenticationServiceException var8) { this .logger.error("An internal error occurred while trying to authenticate the user." , var8); this .unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, var8); return ; } catch (AuthenticationException var9) { this .unsuccessfulAuthentication(request, response, var9); return ; } if (this .continueChainBeforeSuccessfulAuthentication) { chain.doFilter(request, response); } this .successfulAuthentication(request, response, chain, authResult); } } public void setSessionAuthenticationStrategy (SessionAuthenticationStrategy sessionStrategy) this .sessionStrategy = sessionStrategy; } }
上述的(3)过程,sessionStrategy 默认使用的是新创建的 NullAuthenticatedSessionStrategy 实例,所以在前面我们要求 MobileAuthenticationFilter 使用 Spring 容器中已存在的 SessionAuthenticationStrategy 实例,两种登录方式使用同一个 CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy 实例管理 Session。
✌ CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy#onAuthentication
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 public class CompositeSessionAuthenticationStrategy implements SessionAuthenticationStrategy private final List<SessionAuthenticationStrategy> delegateStrategies; public void onAuthentication (Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws SessionAuthenticationException SessionAuthenticationStrategy delegate; for (Iterator var4 = this .delegateStrategies.iterator(); var4.hasNext(); delegate.onAuthentication(authentication, request, response)) { delegate = (SessionAuthenticationStrategy)var4.next(); if (this .logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this .logger.debug("Delegating to " + delegate); } } } }
✌ ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy#onAuthentication
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 public class ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy implements MessageSourceAware , SessionAuthenticationStrategy public void onAuthentication (Authentication authentication, HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) List<SessionInformation> sessions = this .sessionRegistry.getAllSessions(authentication.getPrincipal(), false ); int sessionCount = sessions.size(); int allowedSessions = this .getMaximumSessionsForThisUser(authentication); if (sessionCount >= allowedSessions) { if (allowedSessions != -1 ) { if (sessionCount == allowedSessions) (5 ) 当已存在的会话数等于最大会话数时 HttpSession session = request.getSession(false ); if (session != null ) { Iterator var8 = sessions.iterator(); while (var8.hasNext()) { SessionInformation si = (SessionInformation)var8.next(); if (si.getSessionId().equals(session.getId())) { return ; } } } } this .allowableSessionsExceeded(sessions, allowedSessions, this .sessionRegistry); } } } protected void allowableSessionsExceeded (List<SessionInformation> sessions, int allowableSessions, SessionRegistry registry) throws SessionAuthenticationException if (!this .exceptionIfMaximumExceeded && sessions != null ) { sessions.sort(Comparator.comparing(SessionInformation::getLastRequest)); int maximumSessionsExceededBy = sessions.size() - allowableSessions + 1 ; List<SessionInformation> sessionsToBeExpired = sessions.subList(0 , maximumSessionsExceededBy); Iterator var6 = sessionsToBeExpired.iterator(); while (var6.hasNext()) { SessionInformation session = (SessionInformation)var6.next(); session.expireNow(); } } else { throw new SessionAuthenticationException(this .messages.getMessage("ConcurrentSessionControlAuthenticationStrategy.exceededAllowed" , new Object[]{allowableSessions}, "Maximum sessions of {0} for this principal exceeded" )); } } }
上述代码中,获取当前用户在系统中的 Session 列表的元素类型是 SessionInformation,而不是 HttpSession,我们查看其源码定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public class SessionInformation implements Serializable private Date lastRequest; private final Object principal; private final String sessionId; private boolean expired = false ; }
可以发现 SessionInformation 并不是真正的 HttpSession 对象,只是对 SessionId 和用户信息的一次封装。对于该类的具体使用,需要查看 SessionRegistryImpl 类。
✌ SessionRegistryImpl
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 public class SessionRegistryImpl implements SessionRegistry , ApplicationListener < private final ConcurrentMap<Object, Set<String>> principals; private final Map<String, SessionInformation> sessionIds; public SessionRegistryImpl () this .principals = new ConcurrentHashMap(); this .sessionIds = new ConcurrentHashMap(); } public SessionRegistryImpl (ConcurrentMap<Object, Set<String>> principals, Map<String, SessionInformation> sessionIds) this .principals = principals; this .sessionIds = sessionIds; } public List<Object> getAllPrincipals() { return new ArrayList(this .principals.keySet()); } public List<SessionInformation> getAllSessions(Object principal, boolean includeExpiredSessions) { Set<String> sessionsUsedByPrincipal = (Set)this .principals.get(principal); if (sessionsUsedByPrincipal == null ) { return Collections.emptyList(); } else { List<SessionInformation> list = new ArrayList(sessionsUsedByPrincipal.size()); Iterator var5 = sessionsUsedByPrincipal.iterator(); while (true ) { SessionInformation sessionInformation; do { do { if (!var5.hasNext()) { return list; } String sessionId = (String)var5.next(); sessionInformation = this .getSessionInformation(sessionId); } while (sessionInformation == null ); } while (!includeExpiredSessions && sessionInformation.isExpired()); list.add(sessionInformation); } } } public SessionInformation getSessionInformation (String sessionId) Assert.hasText(sessionId, "SessionId required as per interface contract" ); return (SessionInformation)this .sessionIds.get(sessionId); } public void onApplicationEvent (SessionDestroyedEvent event) String sessionId = event.getId(); this .removeSessionInformation(sessionId); } public void refreshLastRequest (String sessionId) Assert.hasText(sessionId, "SessionId required as per interface contract" ); SessionInformation info = this .getSessionInformation(sessionId); if (info != null ) { info.refreshLastRequest(); } } public void registerNewSession (String sessionId, Object principal) Assert.hasText(sessionId, "SessionId required as per interface contract" ); Assert.notNull(principal, "Principal required as per interface contract" ); if (this .getSessionInformation(sessionId) != null ) { this .removeSessionInformation(sessionId); } if (this .logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this .logger.debug("Registering session " + sessionId + ", for principal " + principal); } this .sessionIds.put(sessionId, new SessionInformation(principal, sessionId, new Date())); sessionsUsedByPrincipal this .principals.compute(principal, (key, sessionsUsedByPrincipal) -> { if (sessionsUsedByPrincipal == null ) { sessionsUsedByPrincipal = new CopyOnWriteArraySet(); } ((Set)sessionsUsedByPrincipal).add(sessionId); if (this .logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this .logger.trace("Sessions used by '" + principal + "' : " + sessionsUsedByPrincipal); } return (Set)sessionsUsedByPrincipal; }); } public void removeSessionInformation (String sessionId) Assert.hasText(sessionId, "SessionId required as per interface contract" ); SessionInformation info = this .getSessionInformation(sessionId); if (info != null ) { if (this .logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this .logger.debug("Removing session " + sessionId + " from set of registered sessions" ); } this .sessionIds.remove(sessionId); this .principals.computeIfPresent(info.getPrincipal(), (key, sessionsUsedByPrincipal) -> { if (this .logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this .logger.debug("Removing session " + sessionId + " from principal's set of registered sessions" ); } sessionsUsedByPrincipal.remove(sessionId); if (sessionsUsedByPrincipal.isEmpty()) { if (this .logger.isDebugEnabled()) { this .logger.debug("Removing principal " + info.getPrincipal() + " from registry" ); } sessionsUsedByPrincipal = null ; } if (this .logger.isTraceEnabled()) { this .logger.trace("Sessions used by '" + info.getPrincipal() + "' : " + sessionsUsedByPrincipal); } return sessionsUsedByPrincipal; }); } } }
也就是说,用户每登录一个新 Session 会话都会创建一个对应的 SessionInformation 对象,该对象是 SessionId 和用户信息的封装,相关信息会缓存在 principals 和 sessionIds 这两个 Map 集合中。需要注意的是 principals 集合采用的是以用户信息(UserDetails)为 key 的设计,在 HashMap 中以对象为 key 必须重写 hashCode 和 equals 方法,所以前面我们自定义 UserDetails 实现类重写了这两个方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 @Data public class User implements UserDetails private String username; @Override public boolean equals (Object obj) return obj instanceof User && this .username.equals(((User) obj).username); } @Override public int hashCode () return this .username.hashCode(); } }
前面也提到,当用户的并发 Session 会话数量达到上限,新会话登录时,只是将最老会话的 SessionInformation 对象标记为过期,最老会话对应的 HttpSession 对象是在该会话的下一次请求访问时才被真正销毁。而Spring Security是通过监听 HttpSession 对象的销毁事件来触发会话信息集合 principals 和 sessionIds 的清理工作,但是默认情况下是没有注册过相关的监听器,这会导致Spring Security无法正常清理过期或已注销的会话。所以,前面我们在安全配置类注册了 HttpSessionEventPublisher 的 Bean,用于监听 HttpSession 的销毁:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 @EnableWebSecurity public class SpringSecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter @Bean public HttpSessionEventPublisher httpSessionEventPublisher () return new HttpSessionEventPublisher(); } }
自定义使用
✍ 统计当前用户未过期的并发 Session 数量
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 @Controller public class TestController @Autowired private SessionRegistry sessionRegistry; @GetMapping("/test4") @ResponseBody public Object getOnlineSession () UserDetails user = (UserDetails) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getDetails(); List<SessionInformation> sessions = this .sessionRegistry.getAllSessions(user, false ); return new ResultData<>(sessions.size()); } }
✍ 统计所有在线用户
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 @Controller public class TestController @Autowired private SessionRegistry sessionRegistry; @GetMapping("/test5") @ResponseBody public Object getOnlineUsers () List<String> userList = sessionRegistry.getAllPrincipals().stream() .map(user -> ((UserDetails) user).getUsername()) .collect(Collectors.toList()); return new ResultData<>(userList); } }
使用 Redis 共享 Session
这里使用 Redis 来实现 Session 共享,实现步骤特别简单。
✌ 在 pom.xml 中添加依赖
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.boot</groupId > <artifactId > spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.apache.commons</groupId > <artifactId > commons-pool2</artifactId > <version > 2.8.0</version > </dependency > <dependency > <groupId > org.springframework.session</groupId > <artifactId > spring-session-data-redis</artifactId > </dependency >
✌ 在 application.properties 添加配置
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 spring.redis.host=localhost spring.redis.port=6379 spring.redis.password= spring.redis.database=1 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max -active=100 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max -wait=PT10S spring.redis.lettuce.pool.max -idle=10 spring.redis.lettuce.pool.min -idle=1 spring.redis.timeout=PT10S spring.session.store-type =redis server.servlet.session.cookie.name=JSESSIONID
✌ Redis 存储 Session 默认的序列化方式为 JdkSerializationRedisSerializer,所以存入 Session 的对象都要实现 Serializable 接口。因此,要保证前面代码中的验证码 CheckCode 类实现 Serializable 接口:
1 2 3 4 5 6 public class CheckCode implements Serializable private String code; private LocalDateTime expireTime; }
✌ 测试
访问localhost:8080/login/page,查看 Redis 数据库中的 key 数据:
spring:session是 Redis 存储 Session 的 默认前缀,每一个 Session 都会创建 3 组数据,下面进行介绍:
☕️ 第一组:string 结构,用于记录指定 Session 的剩余存活时间
上面的例子中,spring:session:sessions:9bf69e21-ddd6-4c53-b7e6-976c047158cb就是这个 string 结构的 key,后缀的字符串是 JSEESIONID 的 base64 解码值。其 value 为空,TTL 时间为对应 Session 的剩余存活时间,如下所示:
☕️ 第二组:hash 结构,用于存储指定 Session 的数据
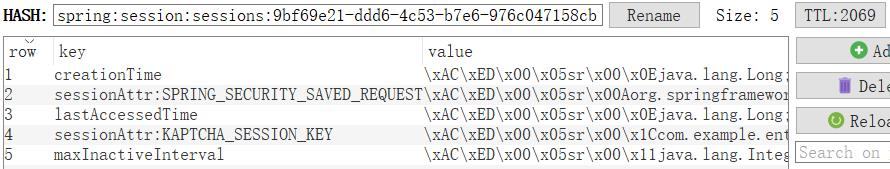
上面的例子中,spring:session:sessions:9bf69e21-ddd6-4c53-b7e6-976c047158cb就是这个 hash 结构的 key,后缀的字符串是 JSEESIONID 的 base64 解码值。hash 结构的 value 值本身就是一个 map 集合,其 value 如下所示:
上图记录分别为 lastAccessedTime(最后访问时间)、creationTime(创建时间)、maxInactiveInterval(最大存活时间)、sessionAttr:属性名 (Session 里存储的属性数据)。
☕️ 第三组:set 结构,用于记录 Session 的过期时间
上面的例子中,spring:session:expirations:1602144780000 就是这个 set 结构的 key,后缀的字符串是一个整分钟的时间戳,其 value 是一个 set 集合,存的是这个时间戳的分钟内要失效的 Session 对应的 JSEESIONID 的 base64 解码值,例如:
remember-me 失效解释
当配置了.maximumSessions(1).maxSessionsPreventsLogin(false)要求只能一个用户 Session 登录时,我们在两个地方使用相同的账号,并且都勾选 remember-me 进行登录。最老会话的下一次请求不但会使老会话强制失效,还会使数据库中所有该用户的所有 remember-me 记录被删除。
第一个浏览器勾选 remember-me 登录后,数据库中 remember-me 记录:
第二个浏览器使用相同账号勾选 remember-me 登录后,数据库中 remember-me 记录:
当刷新第一个浏览器,页面重定向到localhost:8080/login/page?error,显示用户在另外一个地方登录的信息,老会话被强制下线,数据库中 remember-me 记录:
可以发现,该用户的所有 remember-me 记录被删了。
本文转载自:[呵呵233 ]《Spring Security 入门(四):Session 会话管理 》